Dimensional Analysis
Dimensional analysis is a very useful method of converting units from one system to another. This includes units of moles, liters, grams, pascals, meters, and much more. In chemistry, this will be the main use of dimensional analysis.
Example
A concise example of this would be converting measurements of time. Say you want to find the number of seconds in one day. In order to calculate this, you must first set up the problem, which involves indentifying the units you have vs. the units you want.
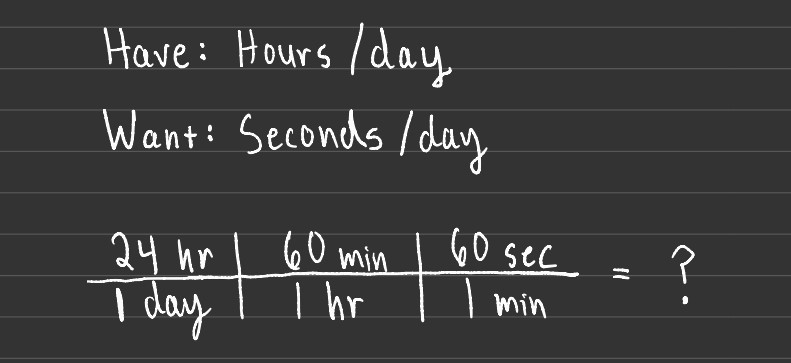
Put the units you're starting with in the first box, then find the conversion factor to the desired unit and place it in the bottom of the next box. This can be repeated several times, as shown in the example. In 1 day there are 24 hours, while in 1 hour there are 60 minutes, and so on.
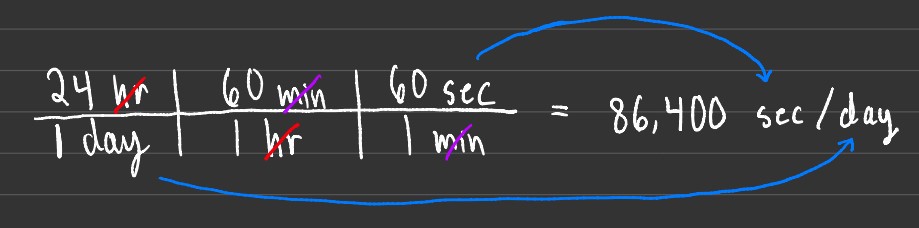
Once you've converted to the point where both desired units exist, start cancelling out duplicate units of measurement. This refers to having the same unit in both the numerator and denominator, which will result in them cancelling. After both the hours and minutes are cancelled, you're left with seconds over days.
Lastly, multiply the numbers in the numerator by each other, and divide the result by the denominator to get your final answer in the desired dimension!