Electromagnetic Spectrum
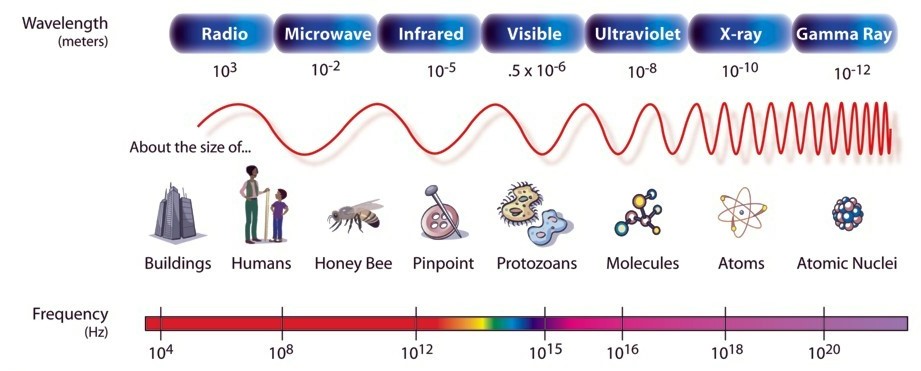
The electromagnetic spectrum is the distribution of electromagnetic radiation based on either wavelength or frequency. This generally is shown by sorting radiation from longest to shortest wavelength, left to right. Wavelength is generally represented by λ (lambda) and measured in nanometers, while frequency is denoted by v and is measured in hertz.
Wavelengths and Frequency
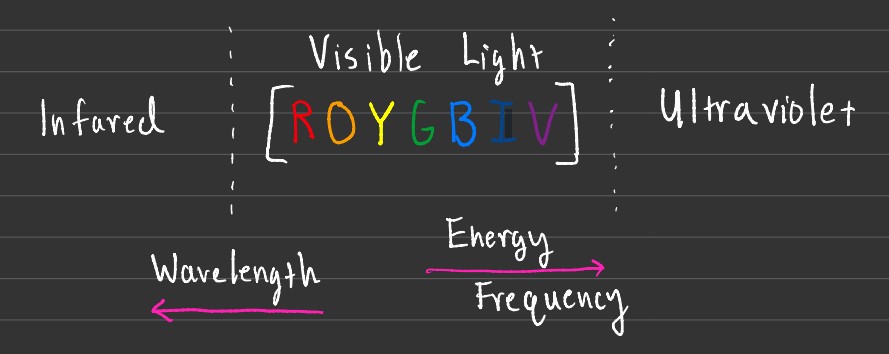
When it comes to visible light, an acronym often used is ROYGBIV, where each letter represents a different color. As you go from left to right along the spectrum, the wavelengths decrease in size, leading to an increase in frequency. This increase in frequency also leads to an increase in energy.
The reason that frequency increases while the wavelength decreases is that the two are inversely proportional, as one goes up the other must go down. Multiplying wavelength or λ, by frequency or v, always results in c, the speed of light which is approximately 2.9979 x 108 m/s.
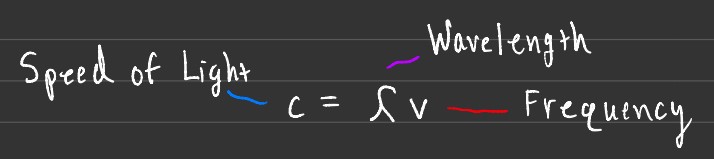
The formula above exemplifies why wavelength and frequency are inversely proportional, the formula is useful when solving for an unknown frequency or wavelength when given one known value. Later on, this formula will become more useful when it can be taken and manipulated to substitute into other equations!