Solution Stoichiometry
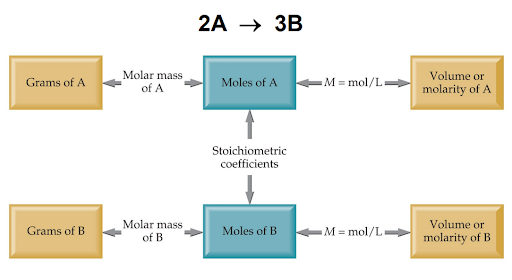
Solution Stoichiometry allows us to quantify the amount of a substance in a solution. Stoichiometry allows us to work in a solution by giving us the concept of solution concentration, or molarity.
Molarity is a unit defined as the moles of a substance contained in one liter of solution. For example, if a solution has a concentration of 1.20 M NaCl, this means that there are 1.20 moles of NaCl per liter of solution.
We can convert from grams of a molecule to its molarity using the diagram above. We can find the molarity of substance B using substance A if both substances have a common chemical reaction that gives us their mole ratios.