Polarizability
Polarizability is a large factor in determining how greatly a molecule is affected by dispersion forces. The heavier a molecule is, the more polarizable it is. As a result, this means that the molecule itself will experience stronger dispersion forces.
Miscibility
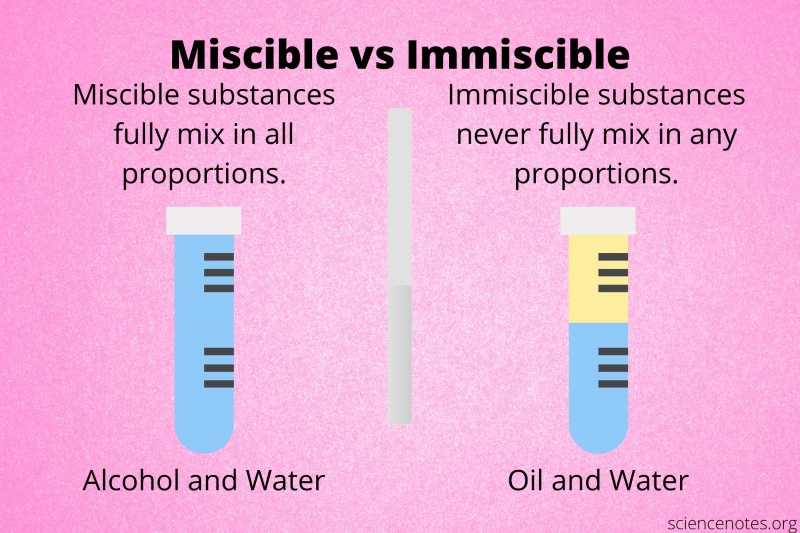
This property describes 2 substances that are mixable together. Something may be miscible if it can dissolve in another substance.
For example, like dissolves like -
- Polar molecules are miscible with polar molecules.
- Non-polar molecules are miscible with non-polar molecules.
- Polar molecules are not miscible with non-polar molecules.