Partial Pressure & Mole Fractions
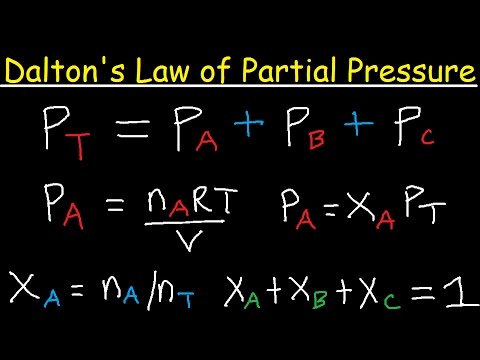
Dalton's Law of partial pressure states that the total pressure of a mixture of gases is equal to the sum of the partial pressures of different gases within the mixture.
Mole Fractions
What this means is that if you find the mole fraction of a specific gas, you can find its partial pressure. To find the mole fraction of a gas xa, find na which is the moles of the gas in the mixture, then divide it by nt which is the total number of moles in the gas mixture. This will give you the mole fraction, and when multiplied by the total pressure, it will give you the partial pressure of the specific gas.
This is shown above in PA = xAPT where PA is the partial pressure of gas A, xA is the mole fraction of gas A, and PT is the total pressure of the gaseous mixture.
Standard Temperature & Pressure
STP or Standard Temperature and Pressure refers to standard measurements or conditions for experimenting with gases. 1 mole at STP is 22.4 liters (Volume), while the temperature is 273 °K, and the pressure is 1 atmosphere.