Acids and Bases
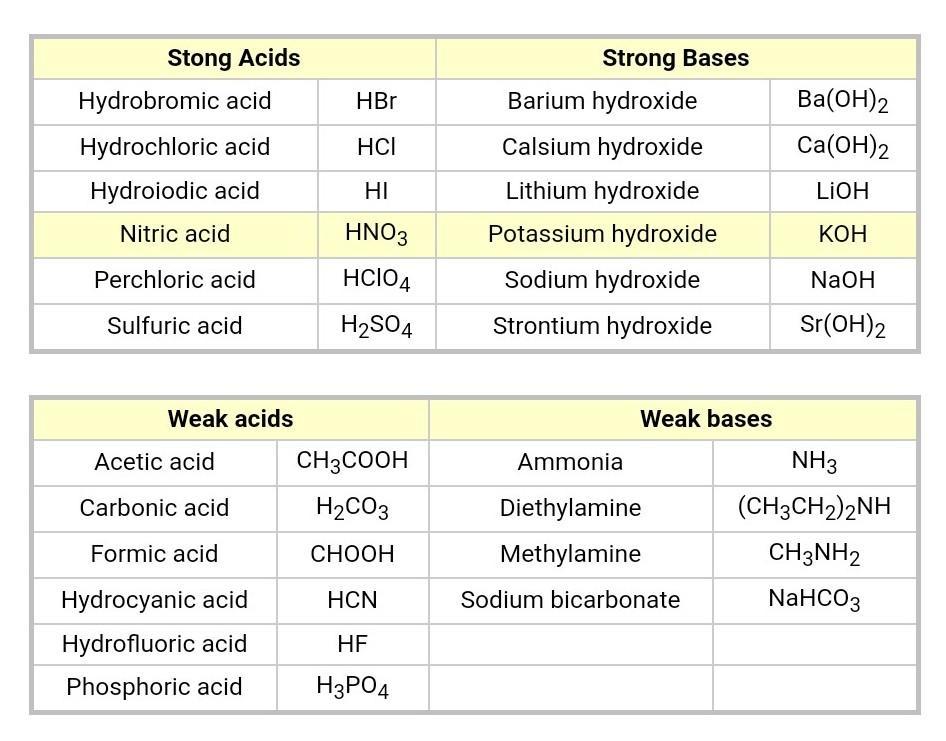
This is a brief overview of acids and bases, with the chart above showing most (but not all) of the strong/weak acids/bases. Generally, strong acids are ions that are combined with an H+, while strong bases consist of ions combined with OH-.
Dissociation and Neutralization
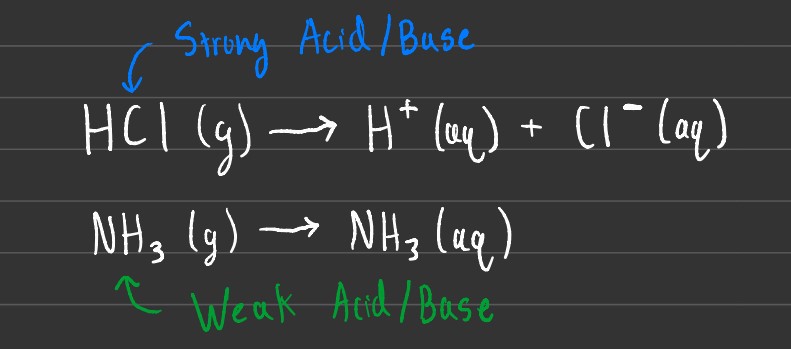
Strong acids/bases completely dissociate inside of solution, meaning that when they are combined with a solvent such as water, the strong acid or base breaks apart into the original ions. This is also known as a soluble ionic compound, talked about in more detail in the solubility section.
Weak acids/bases on the other hand, barely dissociate or break apart inside of solution. This means that when you put a solid or liquid molecule into a solvent like water, the molecule becomes part of an aqueous solution (aq) and doesn't break apart. This is also known as a soluble molecular compound, which was also talked about in more detail in the solubility section.
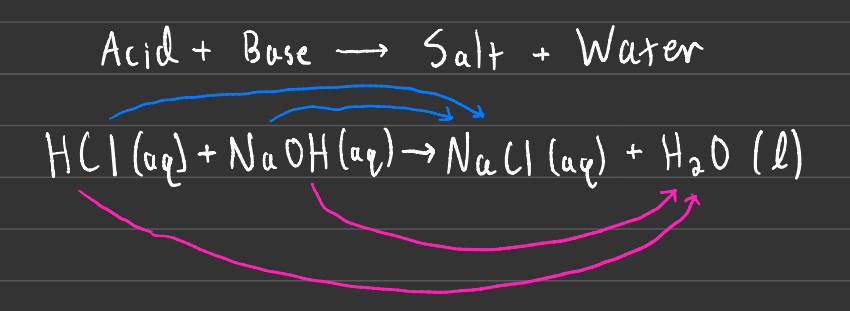
There is also a process known as neutralization, where an Acid and Base react to form salt and water. Salts are ionic compounds that are formed through the reaction, with water being the by-product.